Alternative Data Provider: The Complete Guide To Selling Data
Unlock New Revenue Streams: A Comprehensive Guide for Selling Alternative Data
The rise of alternative data is revolutionizing the finance and investment industries. Data buyers, including hedge funds, asset managers, and corporate enterprises, are increasingly relying on alternative data to gain insights, drive investment strategies, and gain a competitive edge. As an alternative data provider, understanding how to navigate this complex market is essential for maximizing your revenue potential. This guide is your comprehensive resource, covering everything from legal requirements and pricing strategies to trial structures and data delivery methods.
Data Vendor Legal Considerations
FISD (Financial Information Services Division) Compliance
The FISD sets the standard for how financial data should be collected, distributed, and managed. Adhering to FISD standards helps ensure that your data as a data vendor meets the expectations of institutional buyers. Compliance isn’t just about avoiding legal pitfalls – it’s also a signal to potential buyers that you’re a credible and reliable alternative data provider. Data buyers are wary of regulatory risks, so having FISD compliance is a strong selling point.
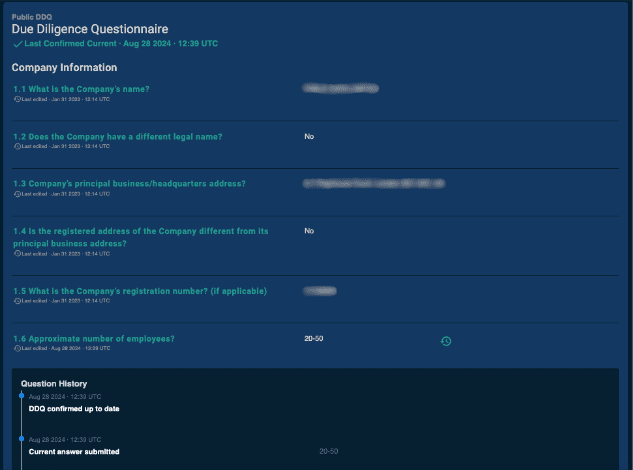
Due Diligence Questionnaire (DDQ)
A DDQ is a structured compliance questionnaire used by buyers to evaluate potential data providers. It covers aspects like data sourcing, collection methodologies, data privacy, and legal rights to sell your data. Prepare your DDQ with thoroughness and transparency to showcase your commitment to compliance and risk management. Providing clear responses about your data collection process, privacy policies, and data sourcing can significantly speed up the onboarding process with data buyers.
Key Takeaway: Ensuring your data is FISD compliant and being ready with a comprehensive DDQ will position you as a trustworthy provider, reducing friction in the sales process.
Understanding Data Buyers and Their Needs
Before you start selling your data, it’s crucial to understand your target market. Data buyers have different profiles, from quantitative hedge funds that require large, granular datasets to fundamental investors who might be more interested in insights and trends.
Types of Data Buyers:
- Quantitative Funds: These funds rely on algorithmic trading and require large volumes of historical data for backtesting and developing trading strategies. They often prefer data that is point-in-time, accurate, applicable to a large investable universe ( typically +75 tickers) and has deep historical coverage.
- Discretionary Investors: Discretionary buyers are more interested in using granular data to inform specific company investment decisions. They may prefer aggregated data, dashboards, or specific insights rather than raw data.
Key Consideration: Tailor your offerings based on the type of buyer. For example, providing APIs with raw data might be more attractive to quantitative funds, while dashboards and data visualizations could be more appealing to discretionary investors.
Pricing Your Data As A Data Vendor
How to Price Your Data
Pricing is one of the most challenging aspects of selling data for alternative data ptoviders. Buyers are primarily interested in the value and return on investment (ROI) they can derive from your dataset. Consider the following factors when setting your price:
- Uniqueness: How exclusive is your data? The more unique it is, the higher the potential price.
- Coverage: The breadth and depth of your data’s coverage (geography, sectors, asset classes) can influence its value.
- History and Frequency: Longer historical data with regular updates is often more valuable.
- Competitor Analysis: Research how similar data sets are priced in the market to avoid under-pricing or overpricing your offering.
Contracting with Data Buyers
When setting up contracts, consider including clauses on data usage rights, and renewal terms. Be clear about what your data buyers can and cannot do with your data. Establishing clear terms from the outset will help avoid misunderstandings and potential disputes down the line.
Key Takeaway: Your pricing strategy should reflect the value, uniqueness, and usability of your data. Aim to offer flexible contracting terms that accommodate different data buyer needs.
Offering Trials of Your Data
Free Trials vs. Paid Trials
Trials are an effective way to introduce buyers to your data. However, deciding whether to offer a free or paid trial can be tricky.
- Free Trials: Ideal for building relationships with potential data buyers. It allows them to test your alternative data without any financial risk. However, free trials should be time-limited to encourage a sense of urgency.
- Paid Trials: Can attract more serious data buyers but might limit the number of potential clients willing to test your data.
Best Practice: As an alternative data provider, ensure your trial period is long enough (at least 3 months) for buyers to thoroughly evaluate your data’s quality and value.
Delivering Trial Data
Data vendors should provide trial data in a format that’s easy for data buyers to access and integrate into their systems. Ensure that trial data is representative of the full dataset’s quality, granularity, and usability.
Key Takeaway: Offer a trial experience that provides sufficient time and access for buyers to assess the data, but also establishes clear boundaries and expectations.
Alternative Data Mapping and Integration
How to Map Your Data to an Entity
As an alternative data provider, mapping your data correctly is critical to its usability. Entity mapping refers to linking your data to specific entities like companies, individuals, or products. For financial markets, having your data mapped to some security identifier is highly recommended. Accurate mapping ensures that buyers can easily integrate your data into their existing systems, making it more valuable.
What Entities to Map Your Data To
The choice of entities depends on your target market. Common entities include:
- Public Companies: Mapping data to publicly traded companies makes it more valuable to financial analysts and investors.
- Geographic Regions: Useful for buyers interested in regional trends or macroeconomic analysis.
- Consumer Segments: Relevant for buyers in marketing, retail, or consumer finance.
Third-Party Companies That Help with Mapping
Consider partnering with companies specializing in data mapping There are many independent technology vendors that can perform this complex task. A partnership can help you streamline the mapping process and enhance the usability of your data. We work with a number of the top 3rd party entity mapping solutions. If you would like to learn more about what the best solutions are and how to get in touch with them, contact us now.
Key Takeaway: Proper entity mapping makes your data more accessible and valuable to buyers, increasing the likelihood of successful sales.
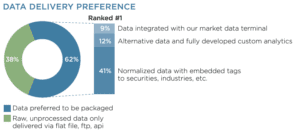
Data Delivery
How to Deliver Data to Buyers Using Snowflake and Similar Platforms
Delivering your data in a way that is convenient, secure, and scalable is crucial for meeting the expectations of modern data buyers. Many buyers prefer using data delivery platforms like Snowflake, which allow them to access data seamlessly within their existing infrastructure. Here’s how to make the most of Snowflake and similar platforms for data delivery:
- Snowflake Data Marketplace: Snowflake allows data vendors to share their data directly through its Data Marketplace. By integrating with Snowflake, you enable buyers to access, analyze, and utilize your data in real-time without the need for complex data integration processes. This makes your data more accessible and attractive to buyers who already use Snowflake’s platform.
- Benefits of Snowflake Integration: Delivering data via Snowflake offers several advantages, such as:
- Instant Data Access: Buyers can access your data immediately, reducing the time to value.
- Scalability: Snowflake’s infrastructure supports large volumes of data, making it ideal for buyers who need continuous data feeds.
- Data Security: Snowflake provides robust security features, ensuring your data is protected during delivery.
- AWS Data Exchange: Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a data exchange platform that lets you share data securely and efficiently with buyers. AWS Data Exchange provides flexibility in data delivery, enabling you to offer data through APIs, downloadable files, or direct integration with AWS services.
- Azure Data Share: If your buyers are more inclined toward Microsoft’s ecosystem, Azure Data Share is an excellent option. This platform allows data vendors to share data in real-time and enables seamless integration with other Microsoft Azure services, making it easier for buyers to incorporate your data into their workflows.
- Google Cloud’s BigQuery Data Transfer Service: For buyers operating within Google Cloud, the BigQuery Data Transfer Service is an effective way to deliver your data. This service facilitates automated data transfers, allowing buyers to schedule and manage data ingestion efficiently.
- Data Delivery with S3 Buckets and FTP/SFTP: While cloud-native solutions are popular, some buyers still prefer data delivered through Amazon S3 buckets or FTP/SFTP for bulk data transfers. These methods are particularly useful for buyers who want periodic updates or who prefer to handle data storage and processing on their end.
Best Practices for Data Delivery on These Platforms
- Optimize Data Formats: Ensure your data is delivered in formats compatible with these platforms, such as Parquet, Avro, or CSV, to facilitate easy integration and analysis.
- Documentation: Provide clear documentation that guides buyers on how to access and use your data via these platforms. This includes details on how to connect to Snowflake, AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud, as well as any necessary credentials or permissions.
- Data Quality and Consistency: Regularly update your data to ensure it remains current and accurate. Consistency in data delivery builds trust with buyers and increases the likelihood of repeat purchases.
Source: FISD Report with Greenwich
Key Takeaway: By leveraging cloud native data delivery platforms, you make it easier for data buyers to access and use your alternative data, increasing its value and attractiveness. A data vendor should offer flexible data delivery options to cater to data buyers who use different data platforms.
Point-in-Time Data
What is Point-in-Time Data?
Point-in-time data represents data as it existed at a specific moment, ensuring that historical records are accurate and unaltered. This is crucial for data buyers conducting backtesting and historical analysis.
Why Data Buyers Want Point-in-Time Data
Point-in-time data allows buyers to perform accurate analyses and test their strategies without the risk of data contamination. This authenticity makes your data more valuable to potential buyers.
Key Takeaway: Maintaining accurate point-in-time data is a significant value proposition for data buyers, especially quantitative funds.
Marketing Your Data
How to Market Your Data
To succeed as a data vendor, you need an effective marketing strategy. Key marketing tactics include:
- Content Marketing: Create blog posts, whitepapers, and case studies that demonstrate how your data can solve real-world problems.
- Networking and Events: Attend industry conferences and networking events to connect with potential buyers.
- Leverage the Eagle Alpha Storefront: The Eagle Alpha Storefront is a platform where you can showcase your data to a global audience of data buyers. It’s a valuable channel for gaining visibility and attracting potential clients.
Key Takeaway: Marketing is a continuous effort for data vendors. Consistently showcase the value of your alternative data through content, events, and strategic platforms.
Conclusion
Selling alternative data is a complex process that requires a deep understanding of your buyers, a robust pricing strategy, compliance with legal standards, and effective marketing. By offering value-driven trials, accurately mapping your data, and delivering it in preferred formats, you’ll be well-equipped to thrive in this dynamic and growing market.
If you want to maximize your data sales potential as a data vendor, contact us today to discover how Eagle Alpha can support you on your journey to becoming a successful alternative data provider.